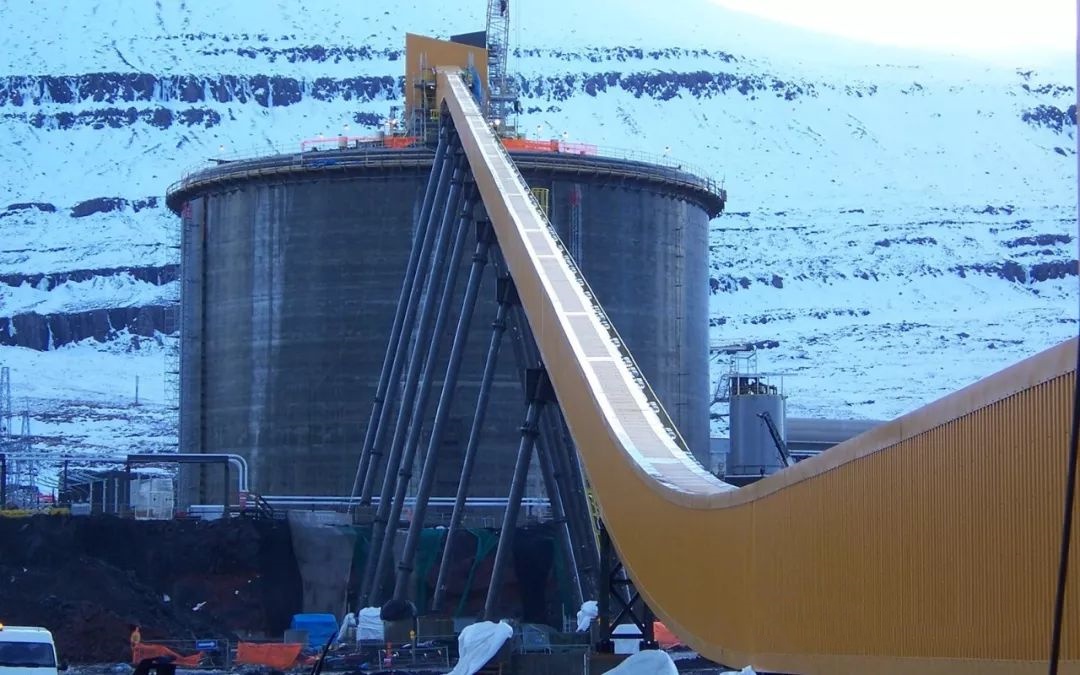

Collapse commonly occurs at convex arc sections due to complex forces,leading to insufficient tension or uneven material distribution.If collapse occurs in straight sections,it indicates a severe problem with the entire belt,suggesting quality or installation issues.Material loading and unloading points can also experience collapse due to concentrated forces.
Causes of Pipe Conveyor Collapse
1.Design Issues:Local collapse usually occurs at convex arcs with small radii,causing the belt to lose contact with the rollers.Initially,the belt is hard and maintains contact,but it softens over time,leading to collapse.Many designs use a minimum of 300 times the pipe diameter for the radius without considering actual softening during operation.2.Manufacturing Issues:Incorrect arc processing,welding deformation,or on-site manufacturing inaccuracies lead to local collapse.Cold bending of arc segments without maintaining design curvature also contributes to this problem.
3.Installation Issues:Incorrect foundation height causes truss buckling,leading to local collapse.Temporary design changes or interference with existing structures during installation can also cause this issue.
4.Usage Issues:Longitudinal scratches or multiple folds in the belt reduce its lateral rigidity,causing collapse.Transporting high-temperature materials can further reduce the belt's lateral rigidity.
5.Belt Quality Issues:Insufficient lateral rigidity in the belt's design,combined with material fatigue over time,leads to collapse.
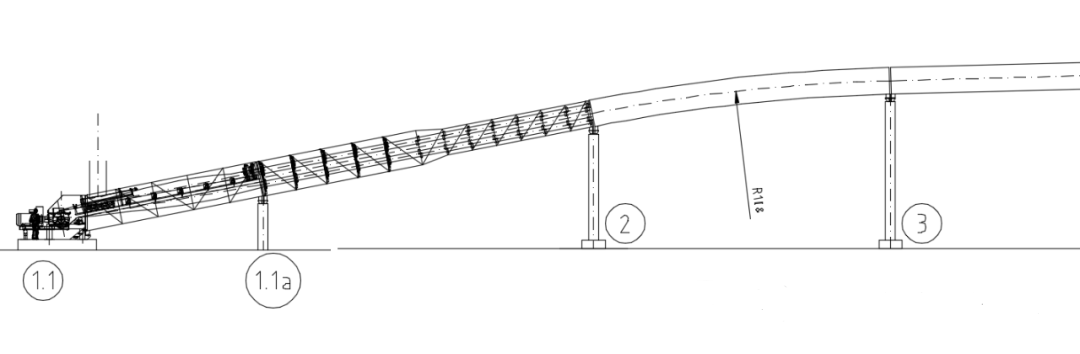
How to Prevent Pipe Conveyor Collapse
1.Design:Optimize the convex arc radius,using the largest feasible radius to ensure good contact between the belt and rollers.Increase the transition section length to reduce edge tension.Use professional design software or discrete element analysis tools for dynamic simulation,ensuring the convex arc radius maintains contact with all six rollers.Allow extra space for adjustments,ensuring the conveyor's outer edge has enough clearance from buildings.2.Manufacturing:Strictly control the curvature of the main chord of the truss to prevent deformation after cold bending.Use auxiliary tools during welding and conduct aging treatment to maintain accuracy.Perform quality checks before delivery to ensure trusses meet design requirements.
3.Installation:Verify all foundation heights before installation,ensuring smooth transitions at truss connections to avoid sharp angles.Adjust support heights as needed to ensure smooth vertical curves.
4.Belt Supply:Sample test the lateral rigidity of the belt to meet design requirements.If the convex arc radius is small,increase the belt's lateral rigidity.Use high-rigidity,wear-resistant belts for long-term performance.
5.Usage:Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight by covering the truss with color boards or Rain Covers to prevent aging.Control the load to keep it within design limits.For high-temperature materials,control the temperature within design limits.Minimize belt scratches during operation to maintain surface integrity.
6.Detection Systems:Install related detection systems for real-time monitoring and alarms,promptly addressing collapse issues.

 ZOOMRY
ZOOMRY

